India’s distinct cultural environment has given birth to a rich music scene that is fast-growing and ever-changing, but dealing with its gargantuan population and slowly developing telecommunications infrastructure may be key to a lasting legacy.
The average internet user in India spends 21.5 hours streaming music every week – nearly four hours more than the average listener elsewhere. But translating this enormous consumer base into strong bottom-line figures remains a challenge for the industry across the board.
Relatively speaking, India was an overdue entrant into the digital space for music. The late penetration of smartphones, combined with inadequate digital infrastructure made data consumption a premium service only available to the wealthy elite.
That changed in 2016, when telecommunications giant Reliance Industries and its mobile network subsidiary, Jio, entered the market. Following a significant investment by Reliance Industries into fibre-optic networks across India in the preceding years, the launch of Jio brought with it significant disruption to the domestic mobile landscape – namely, all inclusive and unlimited mobile data.
‘Reliance came in, gave away free data, and immediately changed the consumption habits of the average Indian user,’ says Ali Sachedina, general counsel and head of business affairs at JioSaavn, a domestic digital streaming service and itself a subsidiary of Reliance Industries.
‘Before Jio launched, people in India would send a WhatsApp message, turn off their data and turn it back on to receive a message because it was insanely expensive for the average Indian to have a proper data plan. After the launch, whether you were a doctor or a rickshaw driver, people were able to live stream on their phone – whether that was music or video – giving rise to companies like our own.’
Change the Tune
The sudden availability of free data in India had a dramatic effect on the digital environment. From a standing start in 2016, India now ranks as the largest consumer of mobile data globally, helped by the fact that it also boasts the lowest prices for data consumption.
‘This has given billions of consumers access to the internet and legitimate sources of content, which is really driving the legitimate growth of digital music in India,’ says Sankalp Dalal, head of legal at Zee Music Company.
Established two years prior to Jio’s data revolution, Zee Music Company had already snapped up a large chunk of licences for Bollywood music, but saw marked growth following improvements to the availability and accessibility of mobile data.
Similarly, JioSaavn also finds its roots in Bollywood music. Created as the result of a merger between JioMusic, the digital music arm of mobile operator Jio, and Saavn, an entertainment distributor focused on Bollywood and entertainment, JioSaavn is the strongest domestic player in India, accounting for 37.8% of the streaming market. Crucially, the 2018 merger combined two key business strands vital for streaming businesses: licences and users.
With 104 million monthly active users and the rights to more than 50 million tracks, the combined entity boasts a wealth of perhaps the two most important factors in the business. Those two factors are also inextricably reliant on the ability of the company’s counsel to both establish and navigate the complex web of licences. JioSaavn works with thousands of different record labels and music publishers, requiring constant negotiation by the business and its counsel in a constantly evolving environment.
‘There are three key stakeholders in any licensing endeavour: the finance team, who model and understand what our obligations are from a revenue perspective; the content team, who handle the day-to-day operation of the labels and licensors; and the legal team, who need to align everyone’s wants and needs in the agreement,’ explains Sachedina.
‘Legal needs to work closely with the other teams when forming and reviewing the agreements. We have to consider the various implications, especially when it comes to the revenue element and the limitations on a product or service. We have to ensure that everything is aligned, before effectively expressing that to the licensor.’
As the music industry in India evolves, achieving alignment across the business functions will become increasingly imperative. Like in many growth industries, short-term profitability – particularly when the entities are well funded – is often cast aside in favour of prioritising factors that will lead to long-term revenue growth.
In the digital streaming space, expanding the userbase and catalogue of licences are the top priorities. But, unlike in other industries, the nature of licensing – particularly in a global environment in which other jurisdictions have already reached maturity – means that costs are a major consideration from the outset. Compensation is generally determined in terms of the number of times the property is streamed, meaning that for each user listening to music, there must be an associated model for contributing towards the costs incurred.
‘Margins are getting smaller. A fair amount of our revenue goes to pay content licensors, both on the music publishing and on the sound recording side. It compels us to look at other avenues of revenue generation and ways to add to our bottom line,’ says Sachedina.
‘As legal, we need to look at everything from a risk management, compliance and value-enhancement standpoint. If there’s a new pricing structure we want to address, we have to look at it through a legal lens and how it affects us in our other endeavours. This requires us to have an absolute knowledge of the business.’
Face the Music
On a global level, as the music industry shifts towards a business model predicated on mass consumption via digital streaming – one where artists are compensated based on the number of times their properties are played – the potential of India and its 1.3 billion people is vast, with international players taking notice.
‘In the past, we were able to convince labels and licensors that India operates with a very unique set of circumstances – the userbase is different and their consumption patterns are different,’ explains Sachedina.
‘Now we’re getting to a point where the labels and licensors want us to operate on the same level as other streaming services around the world.’
Driving that change has been the entrance of major global players into the Indian market. Earlier this year, Spotify and YouTube Music both officially came online in India, armed with deep pockets, expansive licences and best-in-class technology – as well as different value propositions for consumers.
‘If there’s one challenge that any music streaming service or content licensor has, it’s YouTube. You can’t argue with its scale or that their rates are so low – after all, it’s hard to compete with free,’ says Sachedina.
‘The challenges from a content perspective are large, but it’s primarily a pricing problem. The issue is with the Indian community itself: getting them to attribute value to a platform or service that delivers music. The difficulty lies in getting your average Indian user to see value in a premium service because, quite frankly, if it’s free – why should they pay for music?’
It is this struggle to compete with ‘free’ that has dominated the conversation around digital music services, particularly in India. Services like JioSaavn offer their platform for free, but give users the option to pay a subscription fee to gain access to a premium service – unlocking exclusive music, offline features and higher quality streams, in addition to eliminating advertisements.
Out of the 150 million active music streaming users in India, those who subscribe to fee-paying platforms make up only about 1% at present.
‘There are about one million paid subscribers, meaning there’s huge growth potential there. But they need to figure out a model which appeals to the Indian consumer. In my view, streaming services in India will need to find a hybrid between subscription and advertising models in the long term,’ says Dalal.
The challenge comes in convincing consumers that the premium option is worth paying for. The widespread accessibility of music on platforms like YouTube and the sizeable amount of pirated music create substantial problems in encouraging consumers to pay a fee for the additional benefits.
‘The traditional model of the free user and the paid user was that you could download music and listen to it offline. But as connectivity increases and improves, the advantage is lost,’ says Vijay Basrur, founder of OK Listen!, a digital platform for independent artists to earn money through streaming.
‘I think a lot of businesses are now trying to have a subscriber model drawn by original content, or an equal system around music which could extend further than any existing pure streaming services. Businesses like JioSaavn, Gaana, Amazon or Apple – everything is part of a broader system play. They have the benefit of bundling the music together with other services, which helps them by not allocating the entire subscription costs.’
Beating the Black Market
Shifting consumers on to platforms for the legitimate and legal consumption of music is a potential game changer for the industry. Both premium and freemium revenue models capture market share that was previously lost to piracy, bringing new sources of revenue into the mix that were unattainable before the advent of streaming.
‘In 2008, music was primarily consumed on phones via Bluetooth and pirated tracks. Outside of that, the industry was purely physical media sold at an incredibly discounted rate – the markup was set at a bare minimum, yet there was still rampant piracy,’ says Sachedina.
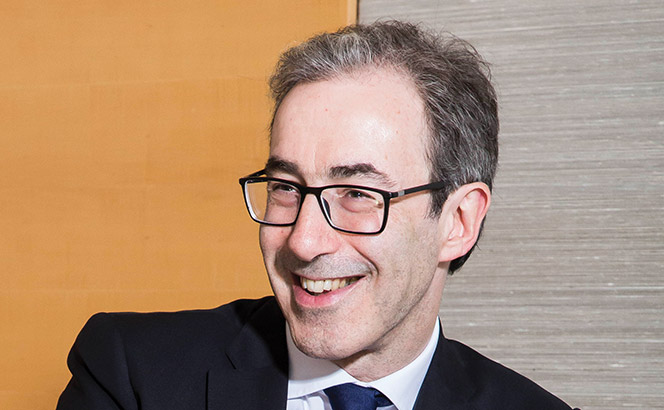
Ali Sachedina, General Counsel and Vice President of Business Affairs, JioSaavn
Taking an unusual path to the top legal job at Indian streaming site JioSaavn, Sachedina discusses his journey into music.
‘Before I joined Saavn, I started my career as a criminal defence lawyer. I was obsessed with music, but moved to New York City and worked in compliance at a bank – and it wasn’t for me. It was at that time I decided I was going to jump straight into the music industry. I wrote to a guy who was managing one of the artists I really liked. I ended up becoming his intern and went from a six-figure salary to zero for two years, but I was happier than I’d ever been.
I started managing bands, but I didn’t really understand how law, music and media tied in together. Eventually, I met a lawyer who had worked in the music business for almost 40 years and was working in-house for the company that managed Aerosmith. He was an old-school, Irish lawyer who told me: “I’m not going to pay you, but what I will do is teach you everything you need to know to set up your own shop.” That’s how I started my career in the music industry – as a lawyer, at least.
I went to India for the first time in my life in 2002. Over the course of a number of trips, I started meeting artists and musicians, helping them understand their IP rights, what to look out for in terms of management deals and recording contracts. At the same time, I had a practice in New York primarily representing hip-hop artists, bands like Mobb Deep and artists out of Canada. I was working on an entire spectrum of deals – anything that came my way, I’d do it.
Working with South Asian artists, I had heard of Saavn and had even done panels with some of their members. Then I started negotiating deals against them – representing artists who were being signed to the various programmes they had. In 2017, they approached me about being their general counsel and the rest is history. I’ve been here since April 2017, so it’s not a long tenure, but it’s been an incredibly sharp learning curve for someone who was living a very rock-and-roll lifestyle as a music lawyer!’
‘Piracy was tackled really effectively by Bollywood, where there was a physical product: DVDs, CDs or tapes. They would literally have police going out and shutting down pirate stores.’
The fact that music piracy has primarily moved to the digital realm does make tackling it a more involved process, but Sachedina points to the success of shutting down illegal cricket streams as evidence that it’s a solvable problem.
‘There’s nothing bigger in India than cricket. Hotstar deliver that content exclusively and have been very effective in stopping pirate cricket and World Cup streaming through a combination of both legislative and judicial orders,’ says Sachedina.
‘Music has yet to be given that sort of push, but that is changing. One of the reasons is because music industry organisations that represent us haven’t, until recently, made it a focus. At Saavn, we’ve been proactive in speaking to labels and helping them understand that piracy is a real issue. Not only this, but it’s an issue that, if properly addressed, would be of benefit to everyone.’
Cracking down on piracy has the ability to have transformative economic effects.
In 2014, it was estimated that 99% of all music in China was obtained illegally. Subsequent action by Chinese authorities resulted in millions of songs and a swathe of websites being taken down overnight, as well as commitment to ongoing enforcement.
Since then, China’s music market has transformed. Tencent Music, the music streaming arm of Chinese internet behemoth Tencent Group, counts 644 million monthly active users across its platforms and controls more than 70% of the market. Since its 2016 launch, the business has been spun off and floated on the New York Stock Exchange, with a $24bn market cap.
‘All we have to do is look at China, who were trendsetters with what they did. The proof was in the pudding: there is immense value in tackling piracy,’ says Sachedina.
‘We’re still missing an effective judicial and legislative protocol to address piracy, but the Indian government has been incredibly receptive. They’re getting ahead of the curve, but it will require a joint effort with the industry bodies in India. We need to find a solution that maintains neutrality – not being draconian by implementing a stringent anti-piracy regime that impedes personal freedoms or access to content but, rather, a balancing act.’
While a series of legislative responses will take time to materialise and be enforced, positive signs are being seen from the judiciary in getting on top of piracy.
‘The Indian courts are being proactive,’ says Dalal, noting that even small procedural changes can have a marked impact on the workload of counsel.
‘Recently, the Delhi High Court passed an order so that when infringing websites have been blocked, content owners only need to go to the registrar of the Court to then block any mirrored sites. You no longer need to keep going back to court to ask after an injunction for affiliated sites.’
Clear as a Bell
Barely three years on from Jio’s data revolution, India can now count itself as one of the most attractive markets for digital streaming globally. While revenue models and legislation are yet to reach maturity, the rapid development of infrastructure and subsequent change in consumption habits are causes for optimism.
‘I think we’re only just scratching the surface in terms of music’s potential in India, as now there’s an audience and an ability to reach them very easily,’ says Basrur.
‘There is an issue with revenue: monetisation can be particularly hard, especially when you deal with independent artists like we do. But we have already seen a massive change. If we take ten years as a measure of time, we have witnessed a massive shift occur in just the last two years.’
‘At present, music in India is getting around five billion streams every month. I expect that to rise to at least ten within the next couple of years, opening more opportunities for businesses and customers,’ adds Dalal.
The pace of change that has occurred in India, combined with the only very recent entrance of major global players, means that a maturation and sophistication should be expected as the industry settles in. But in order to capture that potential, ensuring that the regulations and legislation keep pace with innovation will need to be a priority.
‘We are moving at an accelerated rate, but I’m not sure that all of our infrastructure from a legal, compliance and regulatory point of view is in order; at least in a way that’s best for the Indian user,’ says Sachedina.
‘I do think that’s going to take a year or two to get ironed out and dealt with properly, but it’s getting there. I’m very optimistic about the future of streaming and content delivery.’



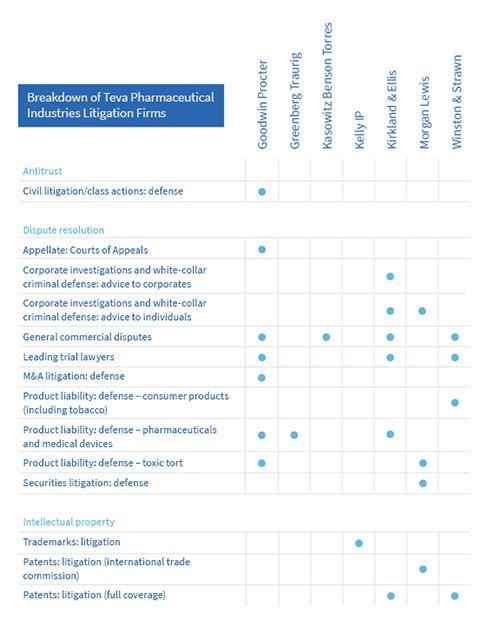 ‘We wanted to have transparency, we wanted the firms to know what we were doing,’ says Stark. ‘With some firms, we have very strong relationships. It’s no comment on our current firms, but we aren’t going to move work around for the sake of it. It’s got to be a compelling reason, at a similar or lower cost. Firms that we are currently working with should see this as an opportunity.’
‘We wanted to have transparency, we wanted the firms to know what we were doing,’ says Stark. ‘With some firms, we have very strong relationships. It’s no comment on our current firms, but we aren’t going to move work around for the sake of it. It’s got to be a compelling reason, at a similar or lower cost. Firms that we are currently working with should see this as an opportunity.’















