The battle to build a diverse, highly skilled workforce, particularly at the leadership level, is continuing around the world – and India is no exception.
Female representation within the Indian legal profession is strikingly low. At present, only three female judges (of 31) sit on the Supreme Court of India, and only 6% of high court judges are women.
46% of those surveyed in Monster’s Women of India Inc study felt that there was an obvious perception that women cannot put in the same hours as men in the workplace. Remarkably, only 72% of men surveyed felt that both men and women ought to receive equal opportunities at work.
Although India ranks fifth lowest in the world in having females in leadership roles according to Women in business: beyond policy to progress, a 2018 Grant Thornton report, this figure has risen from 14% in 2014 to 20% in 2018.
But progress is gradual.
Workplace gender and cultural bias
The prevalence of scepticism regarding a female lawyer’s professional capability and counsel is reflective of gender bias at several levels, with female lawyers often labelled as ‘aggressive’ or ‘unfit’.
A high-profile example of this came in 2012, when comments made by a high court judge caused outrage throughout India. Justice Bhaktavatsala of Karnataka High Court was reported as saying that an unmarried advocate arguing a matrimonial case was unfit to argue, as she was an unmarried ‘spinster’:
‘Family matters should be argued only by married people, not spinsters. You should only watch. Bachelors and spinsters watching family court proceedings will start thinking if there is any need to marry at all. Marriage is not like a public transport system. You better get married and you will get very good experience to argue such cases.’
Following a successful petition, Justice Bhaktavatsala was removed from sitting on family matters.
Zia Mody, founder and managing partner of AZB & Partners, India
‘The foundation of my pathway into law was laid down when I was fairly young. I used to sit on the dining table over dinner and watch my father, who was a senior barrister (equivalent to Queen’s Counsel), talk to his solicitors about the next day’s matters, what he wanted to argue, what the other side would argue. It was truly exciting.
I am one of the founding partners of AZB & Partners, and the firm was born in 2004. Today, we have become an important pan-India law firm with nearly 450 lawyers. We have grown as India has grown.
Women pursuing leadership roles face the same challenges: lack of time, the need to multitask, the guilt of an absent parent and, sometimes, the inability of their seniors – male or female – to understand the safety net they require at a given point in time.
Mentorship is imperative to create and retain young female leaders. Most mentors today will still be male, so it is critical to sensitise them, to go and engage with them. To be willing to articulate your reasonable demands is absolutely critical to successful retention.’
But institutionalised biases remain: an inherent social prejudice or ‘glass ceiling’ subsists for females wishing to advance in the legal field, including in-house. The Women of India Inc study found that 47% of women reported an inherent view that, once married, women were far less serious about their work. And other stereotypes persist.
‘Today, in India, we’re still discussing “Does she have a voice?” and “Should she be taken seriously?” in the workplace,’ says Preeti Balwani, general counsel for India at The Kraft Heinz Company.
‘One of the most critical things that women face is the fact that stereotypes interfere with them being taken seriously.’
She adds: ‘They also judge you based on your appearance – they believe that a certain type of appearance denotes that a woman may be more invested in her appearance than her work.’
Maternity and demanding work-life balance
With the work day – and perhaps night – split between client meetings, case preparation and court hearings, the life of an Indian lawyer, whether at the bar, bench or in-house, does not readily sync with the demands of raising a family.
‘A major challenge would be managing perceptions and the unconscious bias people have towards flexible working hours. For example, when women return from maternity leave,’ explains Shelly Kohli, assistant general counsel for South Asia, Middle East and North Africa at Levi Strauss & Co.
‘Despite being on call 24 hours a day, seven days a week, we still feel pressured if we have to leave early or come in late, whether it’s because of childcare or any other commitment. I also feel that there is a challenge in being perceived as high potential working flexible hours – this whole stigma around working only when you’re visible is a very big challenge that women lawyers continue to face.’
‘Whilst hiring a woman, management consider if she’s going to get married and have children in the near future,’ adds Balwani.
The Women of India Inc study found that 46% of women felt that taking maternity leave would lead to a view that they would also quit, with 59% describing the transition back to work as challenging. This was due to various reasons: unaccommodating executives, pressure to leave the company and their commitment to work being in doubt.
Debolina Partap, general counsel, Wockhardt Ltd, India
‘I think female empowerment in India is still growing, and that women lawyers are learning to have that work-life balance – understanding that it’s possible to have a professional life as well as a social life and to do justice to both. I think, firstly, you need to be a good mother and a good sister, then a good lawyer. That is something we need to understand – if we are good in our roles – we can be good at everything.
The voices of women are being heard more and more, but there are still miles to go. In India, there are very few women legal leaders at the top – I would say if you looked at the top general counsels in India, there would be 5-7% who are women. Personally, I encourage women in the profession and, where I work, women are the majority.
When it comes to balancing my work and home life, I have very supportive family members – whether it’s my son, husband, parents, in-laws or my other relatives. We give space to one another. We respect our roles and respect what we are doing. I think that’s very important to achieve harmony in the work-life balance, and respect what the other person is doing.
As a GC, it’s my job to help the business grow, but the right way. Whilst our office hours are nine to five, I work at least 16-17 hours a day. Out of these hours, five or six are always with management in an advisory role – advising the board, the chairmen and the managing directors, and on the implementation of various strategies with my co-business partners.
My one piece of advice would be to always be open to learning from anyone, including your most junior colleague. Young professionals look at a problem from a different angle, which sometimes you might miss. If we are not open to their ideas, we could be boxed in. We should be open to any new perspectives from anyone. I have had a lot of reverse learning and up-learning – this way you can learn even what you might not be expected to know.’
But, in 2017, the Indian government modified the 1961 Maternity Benefit Act to increase the length of maternity leave from 12 to 26 weeks to females with fewer than two surviving children. While on maternity leave, a female is entitled to ‘maternity benefit’, a fully paid absence from employment to take care of a child. The amendment also included ‘work from home’, and crèche provisions for companies that employ 50 or more employees.
‘I was thrilled when the 2017 maternity law amendment was finally passed – I think it’s a welcome step,’ says Kohli.
‘These changes actually position India as one of the most progressive countries in terms of providing maternity benefits: enhancing maternity leave from 12 weeks to 26 weeks enables women to combine their professional and personal life successfully without jeopardising their health or job security. I believe there are surveys that suggest that 25% of women lawyers actually forgo their careers after childbirth. These amendments address this challenge quite a bit – it also addresses having crèche facilities and ability to work from home, and I think this will eventually show demonstrable results in the form of more and more women employees coming back to work after maternity leave and helping the retention process.’
But not everyone is uncritical of the changes.
Says Zia Mody, founder and managing partner of AZB & Partners: ‘My thoughts on the 2017 maternity leave provisions are that it provides women with the safety net, which creates a good deal of comfort to them. I think the problem for employers is that they will have to pay six months and if, after that, a woman does not return to her workplace but joins a competitor, well – that’s that!’
Additional financial burden on employers could mean that some corporations are reluctant to invest in female employees, considering maternity leave and other associated benefits as wasted resource.
According to Balwani, there is still more work to be done.
‘The 2017 maternity leave provisions are an improvement on the previous law, considering that the previous law was very rudimentary. The new law has increased the amount of weeks, so without a doubt it’s a step in the right direction. Is it comparable to the maternity leave provisions in countries like Norway? No. We need to look around and see where we stand on the global platform – why is a mother in India at a disadvantage against her peers across the world?’
Gender pay gap
A gender pay gap exists whereby women in India earn on average 19% less than men. According to a Monster Salary Index Report, this gap increases to 30% for highly-skilled occupations. The report also showed that 60% of the working women in India surveyed felt discrimination at work and a third of those felt that they were not easily considered for leadership roles. However, of those surveyed, 71% of men and 68% of women felt that gender equality should be a prime concern within their organisation.
57% of Indian businesses surveyed by Grant Thornton in their 2018 Women in business: beyond policy to progress report, indicated that the Indian government ought to be proactive in its approach and do more to tackle the issue of gender disparity in the workplace and business leadership at a statutory position. Yet, of those 57%, only 31% stated that businesses and government should work in conjunction with each other in the domain of gender disparity.
The introduction of The Companies Act in 2013 made it compulsory for all listed and large public companies with a share of 100 crore or a turnover of 300 crores to have a minimum of one female director on their board in India. This was the first obligatory quota for female board members, covering all fields of employment, including legal.
‘Any kind of regulation such as The Companies Act 2013 requires compliance, and people take compliance very seriously. There has been a significant shift between what started off as tokenism versus actual seriousness about compliance. Some of this was already existent for public listed companies, so it’s still early days, but there is a move in the right direction. It’s too early to judge its success yet. I think if you give it another five years, we’ll be able to really sit back and evaluate whether the Act was successful in driving inclusion,’ says Balwani.
But some, like Kohli, argue that enforcement needs to beefed up:
Shelly Kohli, assistant general counsel for South Asia, Middle East and North Africa at Levi Strauss & Co
‘Compared to where we are now, women lawyers have really come a long way. We are continuing to witness growth in the number of women who are graduating from law school but, for women to carve out a successful career in law, still it appears rather challenging or daunting. There are statistics that suggest women lawyers and partners in top law firms are rather low. On the in-house side, I feel that we have seen better progress. This could be because in-house lawyers generally tend to have a better work-life balance and that there are more leadership opportunities.
There is also a gender wage gap between men and women. I think it is pretty consistent across different professions and so is not unique to lawyers. But, whilst this can vary depending on which industry or how big the company is, I think there are a lesser number of women in senior leadership roles. This makes it extremely challenging for women to find able mentors to guide and help them navigate and climb up the corporate ladder.
I am a big advocate of mentorship. I believe that the importance of mentorship for young female leaders – especially those who aspire for professional development – cannot be overemphasised. The promising thing is that many organisations today structure mentorship programmes where women can learn from each other. I strongly believe that mentors can actually facilitate both professional as well as personal development.
Never hesitate to seek out mentors and sponsors who can advocate for your success. I think, as women, we are always hesitant. We seek out mentors, but we tend to always shy away from promoting ourselves and our work. Remember, too, to be patient. I think a lot of young lawyers can improve on this – they want results quickly, but this is a profession which demands a lot of patience and spending time to build expertise.’
‘Whilst this law, certainly on paper, helps improve inclusion and gender diversity in boardrooms, I feel much ground really needs to be covered. There has been data compiled by PRIME Database which has pulled up corporate reports filed by companies as of December 2018. It suggests that 118 of the top 500 national stock exchange listed companies do not have an independent female member on their board,’ she says.
‘These are not very promising numbers; I’m hoping that companies will implement this more seriously and that would really help women coming into more senior positions in companies. I think it’s a compliance issue and I would like to see how the authorities would react to this.
The Equal Remuneration Act 1976 requires the payment of equal remuneration to both male and female workers. However, eliminating discrimination in the workplace has proven to be a difficult task in practice.
‘We haven’t yet gotten to the conversations around the considerable pay gap. I think there is a very high presupposition that women don’t understand finance and that we as a gender don’t know how to ask for what we deserve,’ says Balwani.
Despite government legislation, representation of women in the in-house legal community is lagging behind. Female lawyers in top roles, including in-house, are still the exception rather than the rule. While overt discrimination towards women in the legal, and in-house, field has somewhat decreased, a common view is that this progress has largely been restricted to box-ticking.
Legislation alone cannot force headway, and organisations committed to genuine change and development concerning diversity within the workplace have aligned their policies with a genuine belief that diversity is essential for the advancement of society.







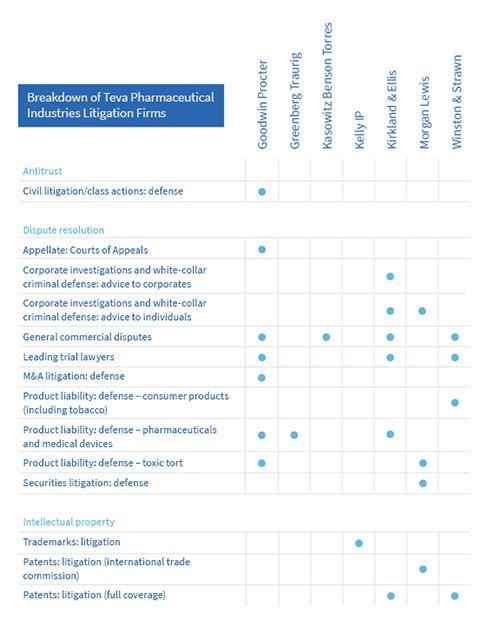 ‘We wanted to have transparency, we wanted the firms to know what we were doing,’ says Stark. ‘With some firms, we have very strong relationships. It’s no comment on our current firms, but we aren’t going to move work around for the sake of it. It’s got to be a compelling reason, at a similar or lower cost. Firms that we are currently working with should see this as an opportunity.’
‘We wanted to have transparency, we wanted the firms to know what we were doing,’ says Stark. ‘With some firms, we have very strong relationships. It’s no comment on our current firms, but we aren’t going to move work around for the sake of it. It’s got to be a compelling reason, at a similar or lower cost. Firms that we are currently working with should see this as an opportunity.’












