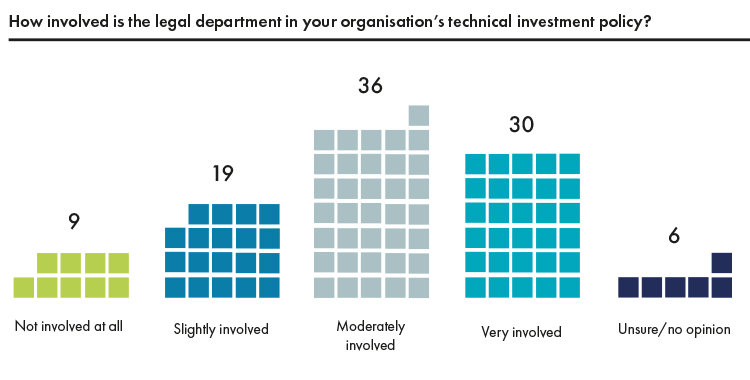
It is not news that the role of in-house counsel has become increasingly demanding and complex. The flip side to that is that the in-house counsel role has become even more strategic, challenging and stimulating than it was 5 or 10 years ago.
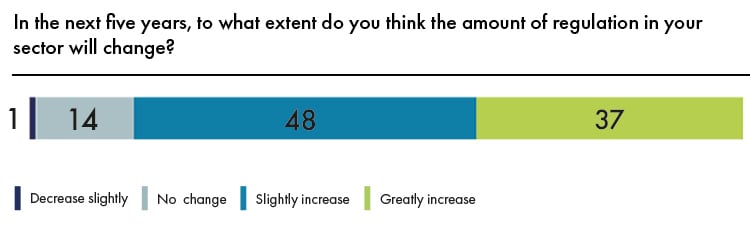
We live in a world which is much more regulated than it was a few years ago, which moves and reacts at a much faster pace than before, in a world where the risks (legal, reputational and others) that general counsel has to help manage, mitigate and protect from are several and diverse in nature.
Below, in summarized form, is an attempt to describe some of the most relevant themes sitting atop of the agenda of general counsel across the country.
Data privacy and cybersecurity issues
The Brazilian GDPR, or LGPD, will soon come into force. At the time of writing, the Brazilian Congress is still debating whether to bring LGPD into force on August 2020 or postpone its enactment to May 2021.
In any event this is a concrete fact in the horizon of all businesses and their legal departments. To the extent these businesses are subsidiaries of companies subject to European or US data protection laws less adaption to comply with local regulations will be required, but at the very least some compliance effort will be necessary.
Beyond LGPD, cybersecurity and electronic fraud in general are increasingly seen as by in-house legal teams, which are called upon to deal with all aspects and repercussions of security breaches of companies’ electronic systems, from a data privacy, consumer and/or criminal law perspective.
Fake news
When we hear the expression ‘fake news’ we usually think of it purely in the political context. The truth is that a number of professionals and business are attacked by producers of fake news everyday with an aim to harm their reputation and gain undue market advantage for competing businesses. In Brazil this huge new problem is compounded by the additional difficulty that the crimes of slander, libel etc and their penalties were designed for a time when fake news would spread by analog means, and thus the potential of harm was smaller. Currently there is a bill of law dealing specifically with the issue of fake news being analyzed by Brazilian Congress and the Brazilian Supreme Court is conducting an investigation on the subject.
Tax Reform
With the Brazilian Federal Government and Congress refocusing on the legislative reform after being sidetracked by COVID-19, the first item on the agenda is the Tax Reform. Each of the Federal Government and Congress have proposed and are supporting different bills of law addressing the tax reform. Until this situation is resolved and a common project negotiated it is unclear if, when and how the reform will shape up.
The new tax rules will be a challenge for everyone until fully understood by market agents and interpreted by the administrative and judicial courts. Some of the changes being potentially contemplated are substantial and can have a significant impact on businesses. The legal and business community are paying close attention to the matter and lobbying for the positions they advocate. The Tax Reform will keep both in-house and external counsel busy for quite a while, before and after the approval of the new rules.
Restructuring
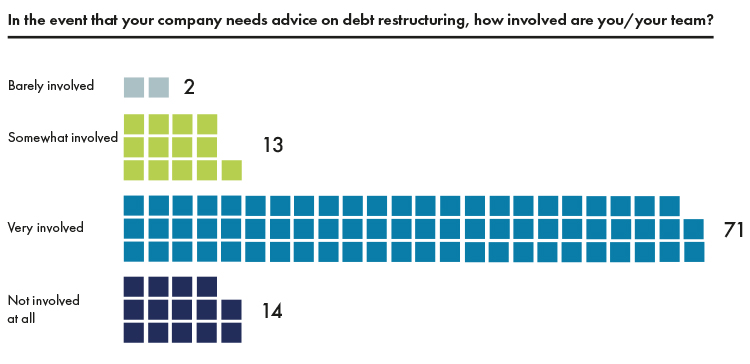
Another challenge/opportunity for in-house counsel is the current situation of financial distress for many businesses provoked by the COVID-19 pandemic. This should allow for exposure on the renegotiation of the company’s debts, and sometimes in the Brazilian processes of Recuperação Extra-Judicial and Recuperação Judicial (respectfully pre-packaged reorganization and court-supervised reorganization), hopefully negotiating with the creditors and approving it with the court, as the case may be, the restructuring plan for the company. Conversely, when in-house counsel is employed by a business that is capitalized and seeking acquisitions/consolidation or debt acquisition opportunities, in-house counsel can exercise their legal creativity to the maximum.
We expect the next couple of years to present plenty of these opportunities, which we know come at a heavy cost for many in-house counsel because it generates the pressure to lay-off part of the team, the fear to lose one’s job and all the mental distress that comes with these situations.
Anticorruption
Since the enactment of the Brazilian anticorruption law in 2013 and the beginning of Operation Car Wash, anticorruption compliance and prevention has been at the forefront of the agenda of most businesses and legal departments in Brazil. This is a trend which came to stay and became part of the day to day of in-house counsel, sometimes adding people to the general counsel’s team and more often simply adding regulatory complexity and responsibility in cases where organizational structures do not provide for a separate integrity/anticorruption function lead by another professional.
The state of ESG (environment, sustainability, governance) in Brazil
The discussion around ESG is still in its very early stages in Brazil, certainly less advanced than in the US or Europe. Nevertheless, after the latest annual letter to investors from the CEO of BlackRock and the endorsements that ESG policies have received by a representative group of CEOs of a number of S&P 500 companies, the finance and business world may be coming to realize the size of the environmental threat not only to our health and planet but also to the economy.
When one recognizes the pressure being exercised on the Brazilian Government in light of the illegal burning and deforestation that is taking place in the Amazon, and the strong reaction of world leaders and private investors – both foreign and domestic – it becomes clear that the environment and sustainable practices, together with good governance, are a much bigger concern than ever before for businesses, their customers and, consequently, the general counsel and her team.
Privatizations, concessions and the new role of the BNDES
Another interesting development we are observing stems from the new role attributed to the National Economic and Social Development Bank – BNDES by finance minister Paulo Guedes.
BNDES in the past would finance, through debt and equity instruments, a huge portion of all infrastructure build-out in Brazil plus virtually all its large corporates. This has changed and BNDES is rapidly divesting of various equity stakes it held in publicly-held companies, state owned or not. The most recent example was a block trade of Vale’s shares for R$8.1bn (approximately US$1.5bn) on 4 August 2020, arguably the largest block trade in Latin America’s history.
Additionally, BNDES is in charge of executing the Federal Government’s privatization program and assists, whenever called upon, Brazilian States and Municipalities with their own privatization, concession and PPPs programs. This is an interesting development which provides in-house and outside counsel alike with ample opportunities.
Similarly, PETROBRAS continues to divest from a number of assets, providing for opportunities both on the acquisition and potential buyers’ finance sides.
New and not so new preoccupations of general counsel
Given the increased pressure to deliver more with less resources, general counsel in Brazil have embraced innovation in general, and technology in particular, from within their own company and also from their vendors, be it a law firm, a legal service provider, a Big Four or a lawtech. Competition has never been so intense, but at the same time there are more opportunities to innovate and create new needs that clients did not know they had.
Diversity is another big item on most general counsel’s agenda. Nothing new, obviously, but relevant, especially in an environment where not only women face challenges, but where the LGBTI+, the black and mulato and purely economically disadvantaged populations are given much less opportunity. It is important to acknowledge that the largest companies and law firms have made good progress in the last few years, which is encouraging. However, there is still a lot to be done.
Two other topics frequently mentioned by general counsels are (i) mental wellness related issues in their companies, in their teams and in the profession, and (ii) pro bono legal work. General counsel are trying a number of measures to keep their people happy and healthy at work and this seems to be a fairly high priority for many of them.
Pro bono became more widespread in Brazil in the last decade and many of the more sophisticated firms run more or less structured pro bono programs. Interestingly, very few general counsel based in Brazil seem to take this into consideration in their hiring decisions compared to their foreign counterparts. We expect this to change and to become more important to them going forward. We certainly hope so as it would be a movement in the right direction.
The changing needs of in-house counsel and the challenges they face inside the company
This article would be incomplete without mentioning the current needs of general counsel and their teams in the challenges they face daily in delivering to their internal clients and other stakeholders of their businesses.
We continue to hear that law firms still tend to think more about what is good for them instead of for their clients. We continue to hear that law firms do not listen, do not innovate and do not engage in true dialogue with their clients as to what their needs are and how they can collaborate together. Conversely and to be fair, we sometimes hear the same speech from managing partners of other firms: that the majority of general counsel do not engage in true dialogue with their firms as to what their needs are and how they can collaborate together.
It seems that someone ought to take the initiative of this conversation. Considering that law firms are the service providers in this relationship and usually well paid to deliver solutions, we are of the opinion that law firms should overcome their old ways and their fear to get in front of the client somewhat vulnerably because they will not have all the answers, venture out of their comfort zone and take the first step. Whoever does that earnestly, consistently and diligently has a much higher chance of success at developing a closer and more meaningful relationship with its clients.
*The author would like to acknowledge the contributions made to this article by his partners, for which he is very grateful.
See more from Veirano Advogados at: www.veirano.com.br/midia